Understanding Redux with React

This is sequence of my earlier post about how to understand Redux in isolation and the problems it solves which cannot be solved by context API. To understand the importance of Redux in depth, here is an excellent article.
▶How to use React with Redux
Redux handles the store creation, middlewares & reducers logic. To use it with React, we need the instance of redux store for all components which is made available through Provider (using Context API). In Order to get the state and dispatch methods from the store we can use the connect from react-redux package. After Redux 7.0 we can use the useSelector and useDispatch hooks instead of wrapping our component with mapStateToProps and mapDispatchToProps.
▶Let's Build a React/Redux Project
We will continue building the project that was discussed in this post, but this time we will build the React UI also.
The project would have UI for two types of accounts: Current and Savings. There would also be a list of bank customers.

To get started we need to install below dependencies.
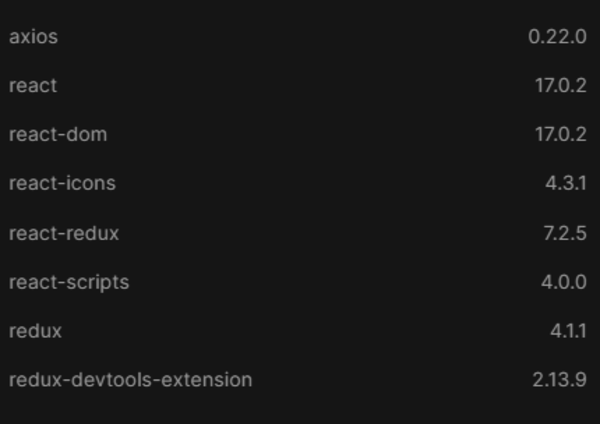
Here is how the directory structure of the project would look like:
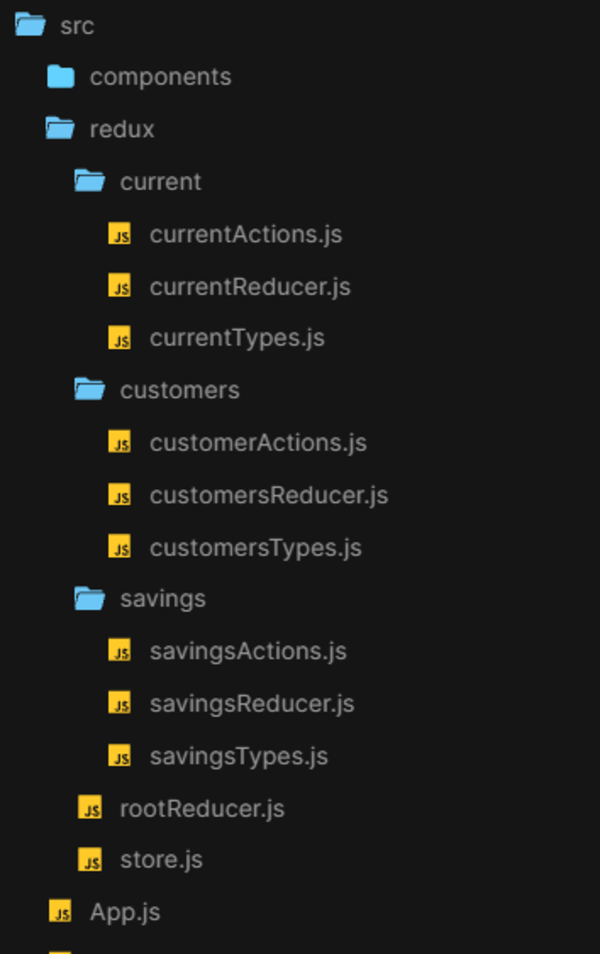
In the previous, we have already seen how to setup action creators, reducers and combining reducers. Here is how the redux store looks like now:
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux"
import { composeWithDevTools } from "redux-devtools-extension"
import thunk from "redux-thunk"
import logger from "redux-logger"
import rootReducer from "./reducers"
const store = createStore(
rootReducer,
composeWithDevTools(applyMiddleware(thunk, logger))
)
export default store
▶Setting up the Provider
To make the Redux store available to all React components, we wrap our App component with the Provider:
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import App from './App'
import store from './redux/store'
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
)
▶Using Redux in Components
With Redux hooks, we can easily access state and dispatch actions:
import React from 'react'
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
import { deposit, withdraw } from '../redux/actions'
const AccountComponent = () => {
const balance = useSelector(state => state.account.balance)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const handleDeposit = (amount) => {
dispatch(deposit(amount))
}
const handleWithdraw = (amount) => {
dispatch(withdraw(amount))
}
return (
<div>
<h2>Current Balance: ${balance}</h2>
<button onClick={() => handleDeposit(100)}>
Deposit $100
</button>
<button onClick={() => handleWithdraw(50)}>
Withdraw $50
</button>
</div>
)
}
▶Key Benefits
- Predictable State Updates: All state changes happen through pure functions
- Time-Travel Debugging: Redux DevTools allow you to replay actions
- Centralized State: Single source of truth for application state
- Middleware Support: Easy to add logging, async actions, etc.
Redux with React provides a robust solution for managing complex application state, especially when you need to share state between many components.